 The heater and stones are the heart of a sauna and the convective loop and löyly cavity they create are its soul.
The heater and stones are the heart of a sauna and the convective loop and löyly cavity they create are its soul.
In a good sauna bathers are heated by an air bath of even convective heat produced by the stones and the stones are heated by the heater. The stones are critical for three things;
- The primary purpose of the stones is to convert as much of the heat produced by the heater as possible to convective heat. Heat is transferred to the stones by conduction, radiation and convection. Then a significant volume of air flowing up through the stones takes on heat from the surface of the stones to become the convective heat that heats the sauna space and us. They act kind of like a primitive or natural heatsink (think cooling fins on electronics) – draining heat off the firebox or electric elements and dissipating that heat in to the air where it becomes the convective heat that we want.
- The stones are critical in producing the steam that is critical to lóyly. When water is thrown on the hot stones, steam is produced and flows with the convective loop. Steam should be produced only from stones and not steel.
- The stones help to soften and even out temperatures over time so that there are not uncomfortable high/low swings. They store excess heat when a lot is being produced and give off that excess when little is being produced (a heat capacitor) which provides a more even and enjoyable heat for bathers.
We want the overall mass and thermal mass in a sauna to be the stones and the heater itself to be as little mass as possible. Aluminum or steel sheet metal that heaters are made of doesn’t do what stones do. Stones are critical.
Nothing makes up for proper stones!
More Is Better. If possible about 6kg / m³ of space is good though some sauna builders in Finland and Sweden I’ve talked with say 8kg / m³ is their target. More is better so 10-12kg / m³ is better up to about 16kg / m³ (or about 1/3 lb / cubic foot minimum to 1 lb / cf). Beyond that may be getting in to some diminishing returns so while perhaps still better, only marginally. More stones, if they are properly heated, result in more even temps, more even softer steam and thus a more comfortable experience. More stones may result in more negative ions which may make us feel better.
On the flip side, it’s important also to not have too much active stone mass for the heating capability of the heater. We want the stones that produce steam to remain about 150 – 250°c or hotter and too much active stone mass might fall below that.
For perspective, a smoke sauna in Finland is recommended to have a minimum of 15kg/m³ (10 liters /m³ ) up to about 90kg of stones per m³. For a ‘small’ sauna of 3m x 3m x 3m the stone cavity would be 65x65x65cm (26x26x26”). For a Banya they aim for 20-40kg of steel and stones per m³ (steel produces a ‘hotter’ and faster steam that stratifies more which is what bath attendants desire in a banya for Perenie rituals).
These targets can be difficult to reach with some heaters, especially the very limited selection in North America, in which case we do the best we can. Maybe 2-5kg / m³ is the best we can do. Also, it is important to not have too large of a heater. Keep in mind as well that a well designed heater with 4kg//m³ can perform better than a not so well designed heater with 6kg/m³.
Olivine Diabase Are Best – Olivine diabase are a volcanic stone that are generally considered the ideal option. Gabro and Peridotite are also good. These heat up well and produce a good convective loop and good steam. Other stone types may not perform well.
Active/Functional vs Decorative/Non-Functional Stones – With tower heaters only the upper stones, those near or above the top of the heat source, are active or functional. The lower stones are mostly just decorative. This does vary a bit by heater. For an electric tower for example, only about half of the stones, the upper half, are functional in producing convective heat and in producing steam. When we say that we need a minimum of 6kg / m³ of sauna volume, that’s 6kg of Functional stones.
Bigger Is Not Better – Stones should be about 5-15cm (2-6”) in size with most perhaps 4-8cm. Surface area is important, too big of stones will result in too little surface area to mass. Too small of stones will not have sufficient mass, will disintegrate and not last long, and will not allow sufficient convective airflow.
Rough and Irregular Is Good, Round Not So Much – Stones should ideally have a rough and irregular surface. This increases their ability to produce convective heat, helps hold tiny pools of water to make better steam, possibly increases heating via conduction and they stay in place better than round. Smoother or rounder stones may not do this so well. If you want the look of rounder stones then maybe use them only for the top our outside layers.
However, Lassi has noted that some Huum heaters that use more rounded stones do produce good löyly. Though rounded, the Huum stones do have a rougher surface which likely helps.
Round Stones Should Not Touch Heating Elements – There is growing evidence that because they shift more over time that rounder stones cause increased damage to heating elements. Cleaved stones do not seem to have this problem.
Commercial Virgin Quarried Stones – Are more likely to perform better and cause fewer problems. They should be of the proper material such as Olivine Diabase, tolerate heat well, and be free of harmful substances.
Landscape stones or river rock may have organic matter (think cow dung) that is unhealthy and can produce unpleasant and unhealthy odors when heated and this can take years to burn out. There is also potential for stones to contain arsenic, asbestos, sulphur or other undesirable elements. Rail ballast often have oils and asbestos so should always be avoided.
Stones from along lakeshores can sometimes be OK if they are of the right material and are not under water constantly (if they have green stuff growing on them you don’t want them). Some of these as well as some commercial river rock do not heat up well and produce a weaker convective loop and weaker steam.
Whatever you choose, wash them well with only water and test burn them for a long time before using with humans present.
Ceramic Stones – These can work quite well though there is some evidence that they can cause the elements in some electric heaters to overheat and break so check with your heater manufacturer before using.
Warm New Stones Slowly – Stones collected in nature may sometimes have pockets of water inside them. Three hours @ 50°c, 3 hrs @ 75°c and 3 hrs @ 100°c with a day or half of cooling down between without anyone in the sauna will allow the water to either dissipate or if the stone is going to explode to hopefully do so without hurting anyone.
Deeply Stoned – You want at least 3-4 courses of stones on top of each other and on top of the heat source. As well, at least 35cm or 14” of depth is recommended. This depth is critical and necessary for both good convective heat and steam. When we throw water on the stones we want there to be enough stone depth that all of the water is converted to steam by the stones and none reaches the fire box. In the case of a heater with too little stone depth it’s possible to use a rain ladle to better spread the water out slower and across the stones to somewhat lessen the harshness of steam created by steel).
Flat Up – Placing stones so that the larger flatter surface is up and very slightly tilted towards the center of the heater will result in the most steam.
Loosely Packed – Air needs to flow freely up through the stones to create the convective heat that we want. They should not be packed too tightly and should not block airflow from vents around the bottom that allow air in to the stone basket.
Seeing Steam Is Not So Good – Steam is invisible. If you ‘see steam’ rising up from the heater that’s not really steam but fog. Fog is comprised of water droplets and does not have the latent heat that is so important with steam. Fog is usually caused by stones not being hot enough – usually due to the wrong type of stones, a poorly designed heater or too large of a heater.
An excellent article from Lassi – valuable for the first loading and replacing: How To Replace Sauna Stones In Your Electric Or Wood-Burning Heater.
And a previous one: How To Know When To Replace Stones.
Harvia also have a good discussion: here.

People in Finland have a specific word for a sauna heater – Kiuas. This is because a sauna heater is different from any other kind of heater or stove. They are indeed the opposite of others. While stoves and room heaters produce a lot of radiant heat and little convective heat and that does work well for that purpose, a kiuas produces convective heat and very little radiant heat.
Kiuas is often translated simply to ‘stove’ in English but that is not accurate. According to a number of sauna experts in Finland I have a high regard for, an accurate translation of kiuas is specifically ‘sauna heater’ so that’s what I use and reserve stove for devices that are indeed stoves.
As we’ve discussed earlier, a sauna is an air bath. A good sauna is heated by convective heat from the stones and the heater that heats these stones, the kiuas, is critical. A sauna heater must:
- Have a properly large and deep stone capacity with significant airflow up through it.
- Heat the stones sufficiently.
- Contribute to the Convective Loop.
- Produce very little radiant heat to the front, back, or sides.
- Keep the heat source close to the floor and the stones low since benches must be above the stones.
- Steam is produced from Stones, not from steel or other elements.
In a sauna you want to experience heat from convection and not feel any radiant heat from the heater. A good convective loop is critical to a sauna as without this the sauna will feel ‘dead’, CO2 and other contaminants will not be removed very well, and our skin can overheat which prevents us from benefiting from the heat.
Radiant heat is uneven and directional, it only heats our bodies on the side it’s radiating from and is very uneven inch to inch and second to second. Heat from convection is more all encompassing. In a well designed sauna it will heat all sides of our bodies evenly which is more comfortable (maintains homeostasis), can help to carry the steam to us via the convective loop, and is what a sauna is all about.
Note: Everything produces radiant heat. There is a lot of radiant heat in a sauna just as there is everywhere around us everywhere we go. We can’t escape the radiant heat that’s produced by the wood walls and even the person sitting next to us. But radiant is directional and uneven so we want to minimize it and keep it as even as possible.
We want as much of the heat produced as possible to rise up as convection airflow and contribute to the convective loop that forms the löyly cavity and as much of this as possible to do so via heating the stones. We want as little as possible to go to the heater carcass which will result in undesirable radiant heat. In other words, we want all of the sides of the heater to be as cool as possible.
This also helps with placement in the room as clearances to combustibles then is less and allows us to get the heater and the stones closer to the heater wall or heater corner which results in a better convective loop and so a better löyly cavity. It is also then a greater distance from bathers which further reduces radiant heat on us. This applies equally to wood or electric heated and hard sided vs open mesh sided heaters.

To choose the best heater for any sauna it’s important to understand a bit about how they are designed.
To produce a good sauna experience, an air bath and good steam, the big ultimate goals are;
- 100% of heat produced by the fire or electric elements goes to the stones.
- 100% of how we are heated is via convective heat (air bath) from the stones.
- 100% of steam is produced from water on stones.
Note that ‘stones’ plays a key role in each of these.
Engineers though must also balance a number of things;
- Good convective heat / airflow.
- Low radiant.
- Intense but gentle steam (typically made from +200°c stones).
- Low height (feet above the stones).
- EU emissions requirements for wood.
Very often achieving one will reduce another so producing a good heater is not easy. A deeper stone cavity might produce better steam but also increases the height.
A couple of important principles:
Heat Is A Zero Sum Game – Any heat from the fire that becomes radiant or conductive is heat that does not go to the stones. We don’t just want to block radiant for instance, but produce less of it to begin with so more heat goes to the stones.
Heat Takes The Path Of Least Resistance – We want to make the stones the path of least resistance. This will result in the most efficient and best kiuas. If heat chooses to flow up in to the stones instead of in to the carcass and radiating out, that’s good.
The design of electric sauna heaters is fairly straightforward as the heating elements can be in the middle of the stones. The stones are the only path. The outer stones stay cooler and help to reduce radiant heat and so most of the heat rises up heating the stones above and contributing to the convective loop.
Wood sauna heaters are trickier because we have a big fire chamber in the middle. The traditional design for these is to have three thin layers on all sides; fire chamber walls (inner carcass) + air channel + thin outer carcass. Thin metal is a path of high resistance so heat largely chooses another option. The air channels also carry heat from the sides of the fire chamber upwards in to the stones. This airflow is critical for the stones, helps the convective loop in the sauna, gets more of the heat produced by the fire to the stones, and reduces the amount of heat radiated to the sides.
While a wood stove to heat a room with radiant heat will be made from thick (1/8” – 1/4”) heavy steel, a sauna heater is intentionally made from much lighter and thinner materials like 1/8” for the firebox, 1/16” for the inner carcass and 1/32” for the outer carcass. The outer carcass being thin does not conduct heat as well as thicker heavier steel and so the stones becomes a least resistant path and this also helps to reduce radiant heat on bathers.
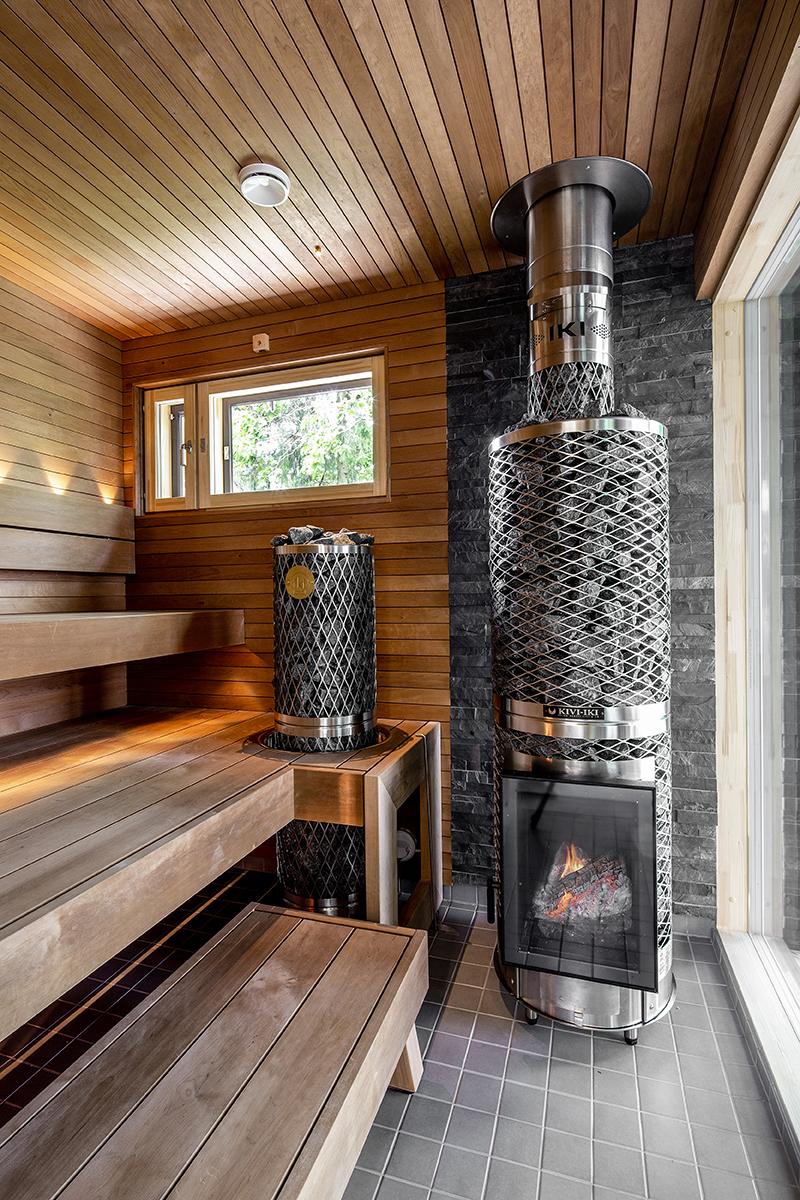
In the following, note how the upper part of the firebox and flue are used to transfer as much heat to the stones as possible to produce the greatest amount of convective heat along with significant stone depth for good convective heat and so that as much steam as possible is made from hot stones before the water reaches any steel in the bottom of the stone chamber.
Here is how this works in a heater from Helo.

And from Harvia: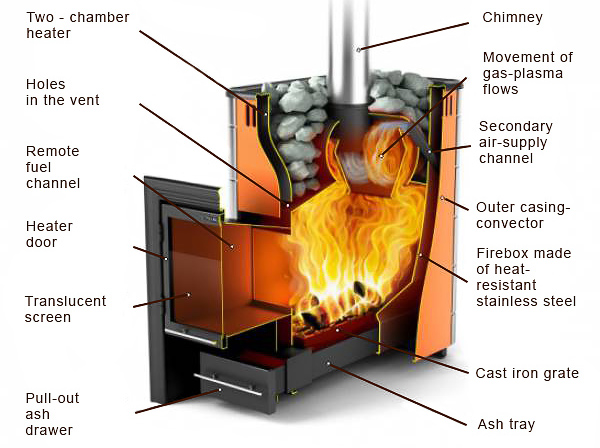
A Narvi NC-20 (by C Macqueron):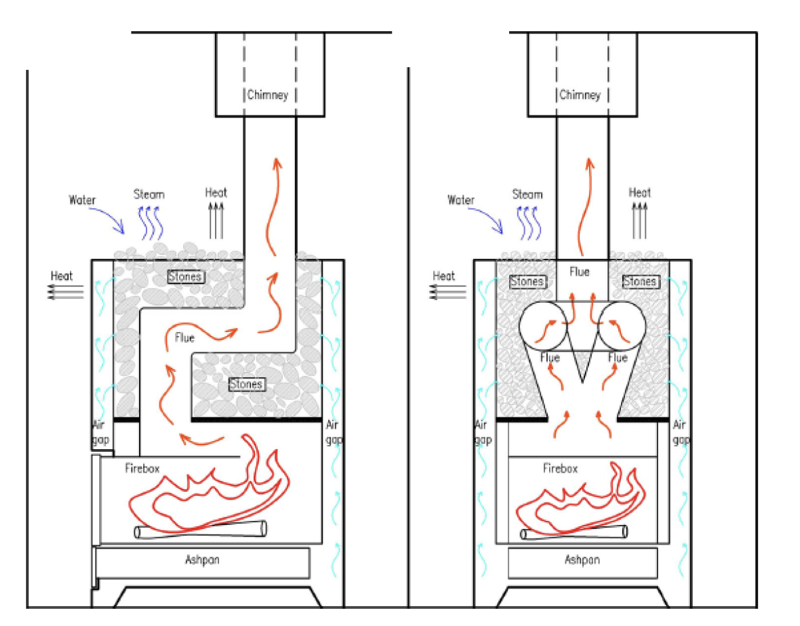
The inside of an Iki. Like others, the firebox is kept very low and both the firebox and flue are designed to transfer as much heat to the stones (and thus become convective heat) as possible.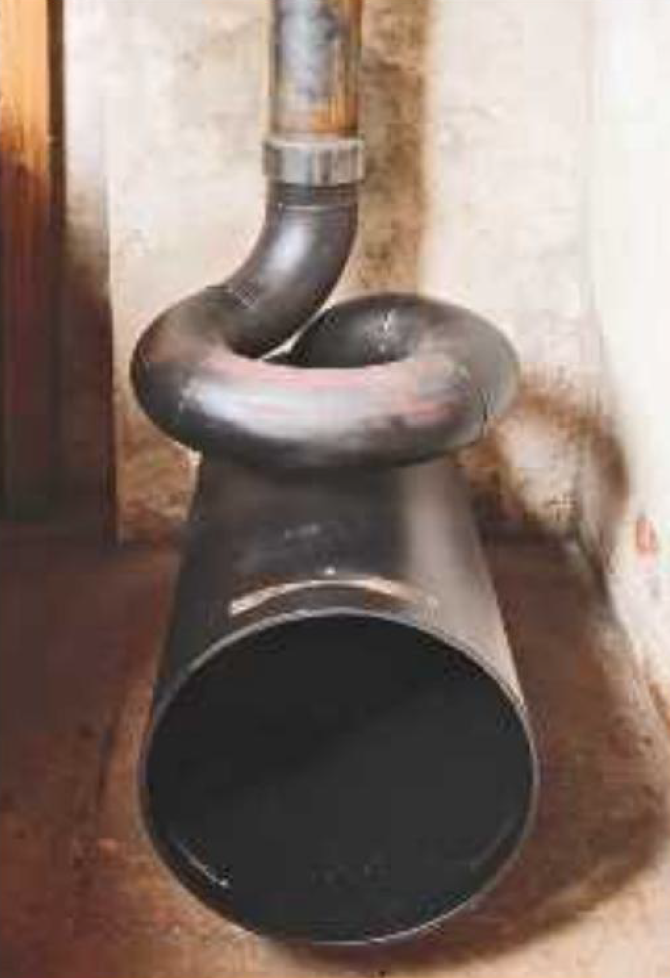 
An alternative introduced by Iki in the late 1990’s is to replace the side air chambers with stones and have an open mesh outer carcass. This further reduces the amount of radiant heat, increases the stone mass and increases the amount of heat contributing to the convective loop. Other manufacturers soon followed with similar designs.
Be Careful – Check The Specs – Some electric heaters aren’t designed to deliver even the 90°c/194°f the UL limits saunas in North America too. Some heaters have very minimal stone capacity. Some produce too much radiant heat. These are all things that make significant differences. A Harvia and Narvi may look the same but perform very differently. There’s a reason better sauna builders in Finland prefer Narvi.
Tower / Column Heaters – These are popular because of their aesthetics but they don’t work so well. We still want our foot bench about 10-20cm (4-8”) above the top of the stones which can result in a really high foot bench. If our foot bench is slightly lower an open sided will usually be a bit more forgiving than a closed sided for temps but not so much for the all important steam.
A shorter closed or open sided will result in a better sauna experience if feet can be above the top of the stones. So a Narvi NC @ 80cm or Iki Original @ 65cm high will be good options. If the benches are too low for those two or similar height heaters then the best option will likely be a Saunum and second to that an open sided tower. A good article by Lassi: Study: A High Heater Leaves Your Toes Cold! and this one: Why Sauna Designers Should Care About The Law of Löyly.

Other than a Smoke Sauna or Aitokiuas, there is no significant difference in the sauna experience between wood and electric if the sauna is built properly. A good sauna is heated by the stones and the stones …don’t really care how they are heated. Someone who is blindfolded will likely not be able to tell the difference in the two. The heat, steam and löyly are the same.
Some people in Finland think it’s funny when Americans with too low of benches and poor ventilation in their sauna say that wood is somehow better. They say that these Americans need to get the sauna log out of their eye before criticizing the speck in others.
Wood is more traditional and more romantic. Wood fires are enjoyable to see, hear and smell (for some). Even the routine of preparing the fire has benefits and for many of us is quite enjoyable, relaxing and a great way to prepare for a good day of sauna – it’s foreplay for sauna. A wood sauna causes you to slow down a bit and be intentional about your sauna. I would argue that there are likely health benefits to a wood fire in that it can be more calming. Wood is the obvious choice for off-grid saunas though improved solar technology is making off-grid electric heated saunas a viable alternative.
The airflow over our bodies in a wood heated sauna can sometimes be somewhat more variable or perhaps punchy than in an electric heated. Some people like this, some not, and most don’t notice. Personally I prefer the more punchy airflow but it’s not a major issue for me.
Drawbacks to wood are that it is not as convenient, uses natural resources (trees), is a direct source of air pollution and more of a challenge to learn. Learning to build and maintain a proper fire along with adjusting vents on the heater and in the sauna might be a bit of a learning curve. Wood heater’s drawing force also varies which requires some trial and error experimentation with ventilation. Some higher efficiency heaters may not pull enough air to provide for good ventilation.
There is also the issue of impact on neighbors – the smoke from a wood heater is fine in a rural area but could be quite inconsiderate in a more urban or suburban area.
Electric is more convenient, especially with a phone app that allows you to begin preheating before you arrive home. Electric can maintain more even temps than wood. How the environmental impacts of wood vs electric compare is a much longer discussion and may depend on how the electricity is generated. From a cost standpoint, a well designed 8x8x8.5’ sauna will use about 8kWh to heat and then about 4kWh to maintain temp during use. So at $0.15/kWh will cost $1.20 to heat up and then about 0.60 per hour so for 2 hrs of use about $2.40.
Electric got a bad reputation early on because of too little stone mass and problems with ventilation. These were corrected by the late 1990’s with more stone mass and downdraft mechanical ventilation. Even so some people still hang on to the idea that electric is not as good.
One significant drawback to electric in the U.S. are the onerous UL requirements and the problems they pose outlined earlier. (2025.07.18 – With UL’s adoption of IEC standards we can hope these problems are behind us.)
Gas is not as prevalent but may be an OK option. It’s critical that a gas heater be well designed and well vented as you don’t want the byproducts of gas combustion in the sauna with you. Some local codes also will not allow remote app control so you don’t have the convenience of electric nor the romanticness of a wood fire.
One challenge with gas may be ventilation. With non-sealed combustion (I believe both Torch and Nippa) these do not exhaust as much air as a wood heater and usually not enough to provide adequate ventilation. Further, I don’t know if it’d be safe to use standard mechanical downdraft as you don’t want to risk any backdrafting of combustion gases. It may however be possible to use a system similar to mechanical downdraft except with mechanical supply to above the heater (in the heater wall facing the bench wall and very near the ceiling) and then passive exhaust from below the foot bench.
With sealed combustion (I believe Scandia) I think mechanical downdraft would be a good option. Scandia are not actually sauna heaters though.
Inside or Outside Feed? With wood you have a choice of loading wood from inside the hot room or outside. With the key benefit of wood fires being aesthetic – seeing and hearing the fire, there is often not a good reason to have an exterior loading heater as it looses that benefit. There are two instances where exterior loading would seem to make sense though. One is an off-grid sauna but where the owner doesn’t want to carry wood in to the hot room. The second is if the loading is done from the vestibule/sitting/changing/shower area where the fire can be enjoyed by people sitting in there.
Hybrid? I built a hybrid gas/wood fireplace for our house. Natural gas is used primarily to get the wood going but is sometimes kept on if wood is greener than it should be. Similarly, it should be possible to create a gas/wood hybrid sauna heater that can act as a traditional wood heater (with a convenient gas starter) or have the convenience of a gas heater when desired.
Ions – One final thought. There has been speculation that a wood heater produces beneficial negative ions while an electric either does not or produces positive ions. There has been no study that I’m aware of to support this nor is there a good scientific foundation for it to be true. The steam that’s created when we throw water on the stones is likely to produce some amount of negative ions and this regardless of how the stones are heated*.
Convenience of Electric and Romance of Wood? – It is possible to have both an electric and wood heater in the same sauna. It requires a bit more space but is doable. The wood heater here is a bit oversized for this sauna as a demo but fun to look at.


Safety Distance & Radiation – A good way to get an idea of how much radiant heat a sauna heater will produce is looking at the safety distances to combustible material (not the safety distance to non-combustible) as this is a measure of radiant heat.
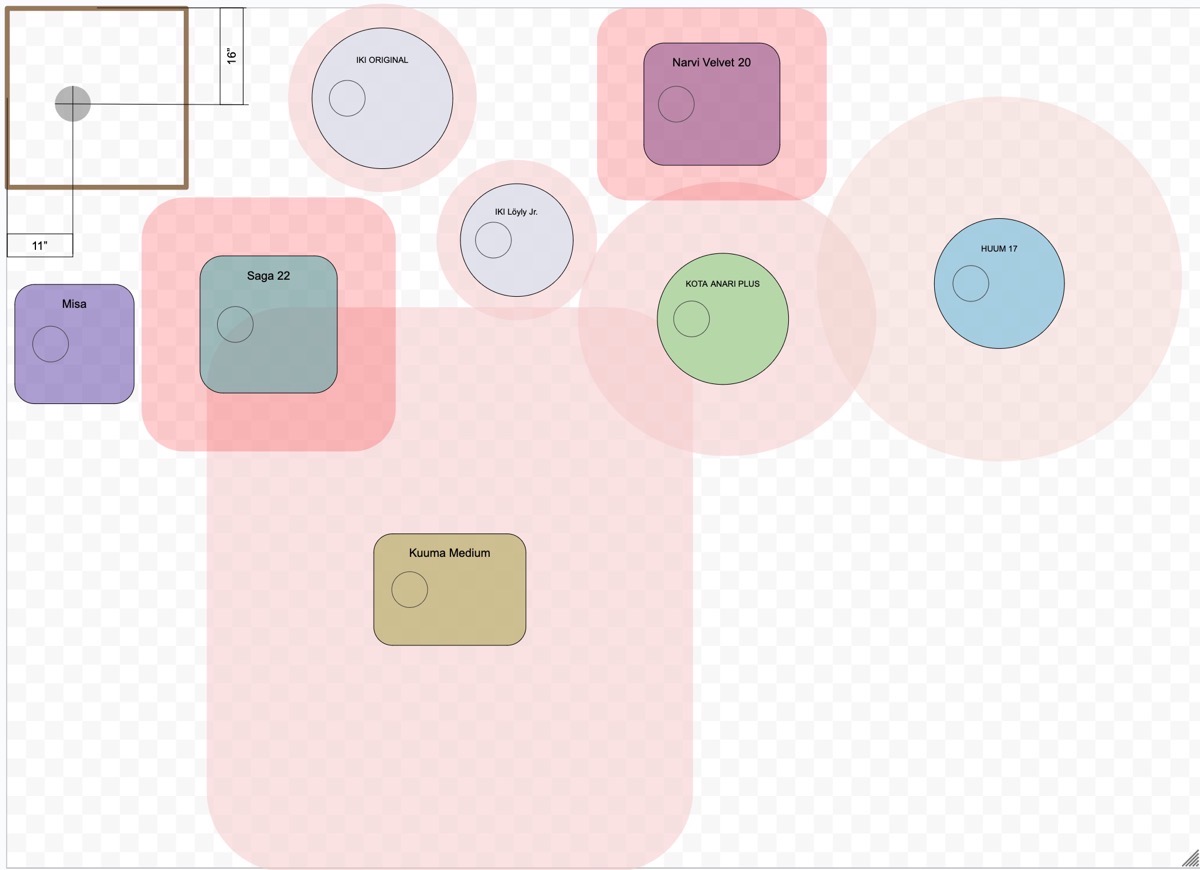 This chart by Christopher ‘Risto’ Rice provides a good glance at how much radiant a few different heaters produce (and why Narvi and Iki are so valued by sauna builders in Finland and elsewhere).
This chart by Christopher ‘Risto’ Rice provides a good glance at how much radiant a few different heaters produce (and why Narvi and Iki are so valued by sauna builders in Finland and elsewhere).
For example, an original IKI is 100mm (4”) to combustibles (largely on all sides) so we know it will produce little radiant heat. A Harvia Legend is 200mm-500mm (8-20”) so considerably more than the Iki. A Helo Karhu is 300mm (12”) on sides and 500mm (20” to the front) and the Harvia Pro 36 is a wapping 500mm (20”) on all sides (though it is intended for quite large saunas where it will naturally be a considerable distance from bathers).
A good rule of thumb is that you want bathers at least 3-5x this distance from the heater and ideally 8x. With most heaters at 5x you can still feel some minimal radiant while 8x achieves the ideal of no noticeable radiant. So at a minimum you want to be at least 500mm (20”) from an Iki, but 2286mm (90” or 7.5’) from a medium Kuuma. Note that there may be an inverse relationship with shorter distances to combustibles needed a higher multiplier like 8x and greater distances to combustibles needing a lower multiplier like 3x.
Some heavy steel stoves don’t shield the front and corners thinking that’s unnecessary but it is very necessary, especially the corners. Heat radiates in all directions from its source so someone sitting at a 45° angle to a stove will feel almost as much radiant as someone sitting directly in front.
For more: Radiant – To Be or Not To Be.

Here is some comparative information on various heaters available in North America. I believe this is accurate but it is not guaranteed.
Best Option? – What type of heater (closed sided, open sided or circulating) is best will vary based on the dimensions of the sauna, particularly ceiling height and how each individual model functions within different spaces. Unfortunately we don’t have good data on how various heaters do with regard to thermal stratification and steam. In other words, how good of a Löyly Cavity each produces in what space.
Feet Above The Stones – Is critical to good löyly for largely all heaters except Saunum. This makes most tower/column heaters a poor choice.
Here is a very rough chart to consider:
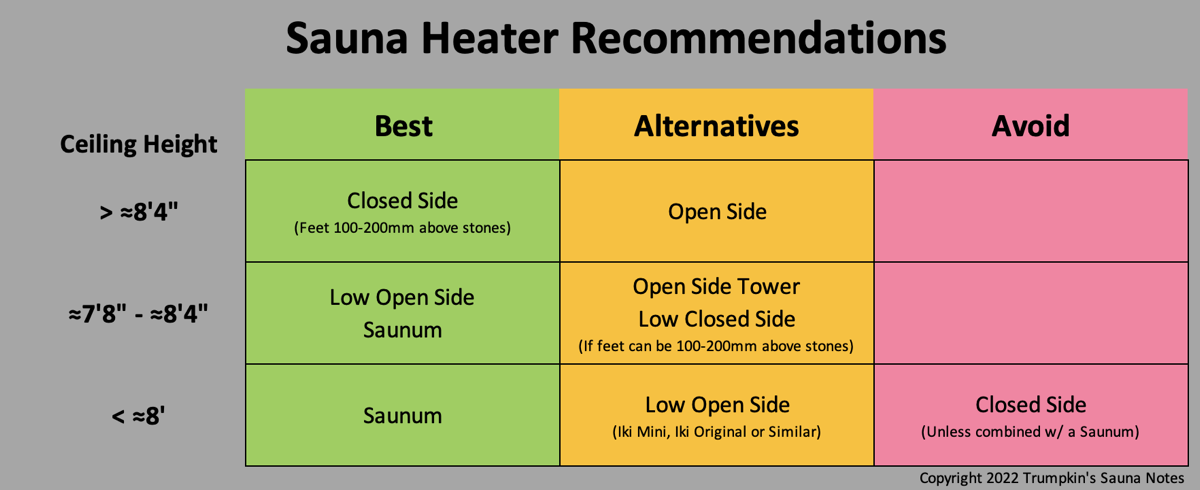
Based on conversations with a number of people in Finland, a properly high ceiling and benches with a closed sided heater provides the best sauna experience (second to a smoke sauna though).
If you can’t get your feet well above the stones of a closed sided heater then a short (not tower) open sided heater may be the next best option. And if you can’t avoid a quite low ceiling then either a Saunum or adding a convection tube to an open sided heater are likely the ticket. Keep in mind also that a Saunum can be used with a wood heater. Some Bio-sauna heaters such as from Klaf’s or SaunaSampo may also work.
A Convection Tube is a duct that runs up the middle of the stone mass of an open sided heater. It pulls air in from the bottom of the stone mass and produces a sort of enhanced convective loop that can help to lower the floor of the löyly cavity (decreases stratification). The duct should be about 8 – 18cm (3-7”) diameter, probably closer to 8cm on most heaters, and run from bottom to top. At the bottom there needs to be a cavity or duct from the edge of the heater to the convection duct to provide airflow and this should face the benches.
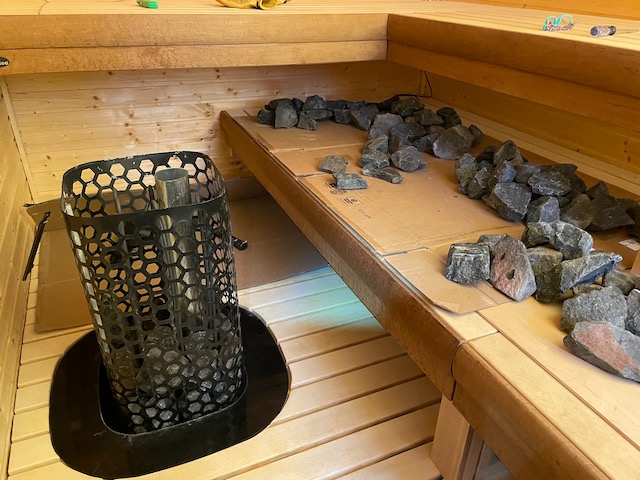

This was originally posited and demonstrated by Sauna_Sitter (Reddit). It is still experimental but early experiments are showing moderately positive results. The photo above is one of my experiments with it in late Nov/Dec 2023 that resulted in about a 4°c increase in temps at the foot bench along with a slight improvement for steam. Note that this is not a replacement for proper bench heights and feet above the stones.
Bigger Is Not Necessarily Better – Too large of a heater can have a number of drawbacks.
- It Will Short Cycle. Electric heaters work by constantly turning on and off. If you’ve set it for 100°c then it will turn on until the sauna reaches perhaps 103°c and then turn off until it has cooled to maybe 97°c when it will turn on again. With a properly sized heater (and lots of stone mass) these cycles are largely unnoticeable but if the heater has too much power for the space then the heating up can happen quite quickly and be noticeable followed by a long period of the elements being off.
- A secondary and bigger problem of short cycling is that the elements are not on long enough to keep the stones sufficiently hot to produce good steam.
- Larger Temp Swings. Rather than 97°c to 103°c, a too large electric heater can result in perhaps 95 to 110 or 115°c.
- More Direct Radiant Heat. In a sauna we want convective heat, not direct radiant heat. The larger the heater (electric or wood) the more direct radiant heat it produces. This isn’t so much of a problem if the heater is sized properly so that larger heaters have larger spaces and can be further from bathers.
- Evenly maintained lower temps allow for a greater range of löyly from dryer to wetter steam. Too large of heaters cannot maintain lower temps well.
- If interior height is tight then a heater on the smaller side may get the stones down lower in relation to the foot bench providing a more comfortable experience while too large of a heater will have the stones up higher so bathers will have colder feet and actually be less comfortable with a larger heater than smaller.
- Fire Hazard. Too large of a heater can be a potential fire hazard.
Finnish RT Guidelines state 1.0kW per m³ (per 35 cubic ft) for saunas below 10 m³ (350 cubic ft) and slightly less for larger spaces. This assumes that walls and ceilings are insulated, that at least 90% of the wall surface and 100% of the ceiling is soft wood and a proper mass of stones in the heater. For windows or other uninsulated wall areas add 1-1.5kW per m² (per 11 sq ft) of window surface. For stone or similar wall surfaces add 0.7kW per m² (8 sq ft).
Now, to maybe contradict myself. Stone mass is critical so sometimes it’s necessary to upsize a heater purely for stone mass.
And in general stay within the recommendations from manufacturers.

An electric heater with a separate wall mounted thermostat sensor provides for a better sauna experience than those with the thermostat sensor inside the heater.
For the best sauna experience, the best mounting location for the thermostat sensor is on the bench wall, ≈1m (39”) above the sitting bench, no more than 10cm (4”) to the ceiling and ≈20-30cm (8-12”) from a corner. So on the bench wall opposite the heater wall. This results in the most accurate and even heat.
Note that there is a cold air buffer next to the wall so the actual air temp at bathers heads might be 4 – 6°c higher than indicated on the thermostat control (good for those with UL listed heaters limited to 90°c). For the most accurate measurement though the sensor should be placed ≈5cm out from the wall.
Mounting the thermostat sensor on the heater wall and particularly near or over the heater per UL and some mfr recommendations results in sauna temps that are as much as 30°c (≈55°f) cooler since this location is measuring the heat rising from the heater rather than the actual sauna temperature. It also results in wider high-low swings, less even temps overall and is less predictable. Because of this, electric saunas in the U.S. are on average about 35°f cooler than indicated on the thermostat and not as comfortable.
Sometimes incoming fresh air over the heater and near the thermostat sensor will cool the sensor resulting in higher temps at bathers heads though also greater and unpredictable variability. This can be an advantage to those with UL heaters but can be tricky to know what the temps will be.
Some heater manufacturers recommend placing the sensor on the heater wall even outside of UL territory. One reason is to lessen warranty costs. Placing the sensor on the heater wall results in lower temperatures for the sauna, less work for the heater and less likelihood of element failure. Another reason is to lessen the risk of fires if the wall or ceiling above the heater gets too hot and combusts.
Caution: Though commonly done in Finland and elsewhere, placing the thermostat sensor on the bench wall may in some cases allow the walls and ceiling above the heater to get too hot and combust. I’m not aware of this being a significant problem however it is something to consider. This would particularly be a problem in the case of a ceiling sloped the wrong way (higher over the heater).
As well, UL prior to UL 60335–2–53, required the thermostat sensor be mounted on the heater wall for UL listed heaters. Placing the sensor other than specified such as lowering it or placing it on the bench wall may void insurance in case of a fire. During rough-in you should run wiring to both locations which will give you options in the future, particularly for newer heaters that might include both a sensor for sauna temp to be placed over the benches and a secondary high limit sensor above the heater.

Bio-Sauna – There are several options for a bio-sauna experience and most of these allow bathers to choose either a traditional Finnish Sauna or Bio-Sauna with an app. Key to these is having a good humidity sensor and control system to maintain a desired constant humidity level, typically about 50-70% relative humidity, in the sauna. Klafs and SaunaSampo are perhaps the best known and I think both work well in my experience and from what I’ve heard from others in Europe.
The Tylö Combi (Sense or Crown) likely results in a less than good experience due to too little stone mass and other issues. I would avoid these until they’ve proven that they can deliver a good experience for both bio-sauna and Finnish sauna.
There are also options for adding misters to traditional sauna heaters that can maintain good moderate humidity. Here are Lassi’s thoughts of the Kastee system on Saunologia.
Helo-WT and Similar ‘Technology’ – Some heaters like the Helo Himalaya include a water tank in the middle of the stones. The idea is that you fill it with water and it then produces constant mild steam and humidity throughout your sauna session. The result is kind of a Bio-Sauna though in my experience it doesn’t provide nearly as much humidity as a Bio-Sauna. On most heaters you can remove the tank, put more stones in the heater and the heater and sauna will function better as a traditional Finnish sauna. With the tank you get constant very mild humidity and because of the lessor stone mass you get a lessor steam when you throw water on the stones. Without the tank you get a more traditional (or proper according to many Finns) sauna that is naturally rather dry with stronger bursts of gentle steam.
Similar to this are systems like the Harvia Combi that have a steam generator or constantly drip water on the stones for a bit higher constant humidity and a more Bio-Sauna like experience though my understanding is that these fall a bit short of a true bio-sauna.
Harvia’s Autodose does not have a humidity sensor nor capability to be controlled based on humidity so will not provide a bio-sauna experience. While I am a fan of automation, auto dosing is not something that I personally feel should be automated (conversely, a bio-sauna does kind of need to be automated). Bathers controlling the environment in a sauna by throwing water on the stones with a ladle is a key part of sauna to me.

Recommended Manufacturers:
- Narvi – Generally considered the one of the best among people in Finland for design, function and build quality. These have a lot of stone mass and depth, produce a good convective loop and good steam, along with very little radiant heat which all contribute to good löyly.
- Iki – Introduced the open sided mesh concept in the 1990’s and makes some of the more well regarded heaters in Finland, the Iki Original in particular gets quite good marks. Note that these all, including the taller towers, still require Feet Above The Stones.
- Helo / Sauna360 – Good build and functional quality. A step below Narvi perhaps but above Harvia. This is unfortunately also a confusing array of branding including Sauna360, Tylö, Kastor, Finnleo and Amerec. This group of companies is now owned by Masco (Plumbing) Corp and mostly under the Watkins Wellness group.
- SaunaSampo – Heat storing heaters with significant stone capacity that can also provide a bio-sauna experience. These can also reduce heat and possibly steam stratification in some cases.
- Harvia – Harvia is generally a good value brand. Lower quality for both build and function but also lower cost.
- Some of their products have a bad reputation for too little stone mass and producing too much radiant heat so that’s something to watch carefully for with these.
- There have been reports of some Harvia heaters not being able to achieve or maintain promised temps.
- There have been increasing reports of elements corroding very prematurely after a few months of use (they should last a couple of decades at least), particularly on KIPs but also others. My understanding is that Harvia are quickly replacing these under warranty with more robust elements.
- The new UL compliant Cilandro with enclosed sides should be avoided as it will likely perform worse than other more open tower heaters unless you can get the foot bench above the top of the stones.
- The new Spirit may be a good option for some saunas though care must be taken when pouring water on to produce steam. Read Lassi’s review here.
- Aino – Some of the more interesting heaters from an aesthetic standpoint. These can work well but hot rooms must be planned carefully to achieve good results.
- Aitokius – Aitokius (owned by Narvi) are specialist single heat sauna heaters favored by sauna connoisseurs. In a well designed sauna and with proper use these produce a sauna experience that is said to be as close to a smoke sauna as possible without actually building a smoke sauna. More here.
- Saunum – For any sauna where you are forced to have a ceiling of less than about 250cm (8’) these are likely the best option. My understanding is that this works equally well for electric and wood. These are available in the U.S. as of March 2023. A good discussion of these is from Lassi here: Case Study: An air circulating heater improves the comfort of a small sauna.
Maybe Recommended:
- Nippa – These I think likely fall somewhere between a Kuuma (original) and what are considered sauna heaters in Finland. The Nippa has more stone depth (top to bottom) than Kuuma and appears to have good airflow up through the stones. This appears to result in a reasonably good convective loop and steam that is less harsh than steel steam and more like sauna stone steam. Similar to Kuuma, Nippa produces considerable radiant heat though so should be placed far from bathers. While a heater from one of the mfr’s above will result in a better sauna experience, Nippa may be an OK option for those who want to buy something made in America and have a sufficiently large hot room.
- I have heard one report from a Finn I trust that they had a good experience in a sauna heated by a Nippa but also noted that it was a very large sauna (10’ x 11’ IIRC) and the heater and its radiant heat were a considerable distance from bathers. I’ve not experienced a Nippa myself but this report makes sense when we look at the design of the Nippa.
- Klafs – Offer a variety of heaters including their Sanarium bio-sauna heaters that in my experience aren’t bad. I would avoid their under bench options. Klafs are now owned by Kohler (Plumbing, Generators, etc.) and their heaters are now apparently exclusive to their not very well designed saunas.
Not Recommended:
- Homecraft – Firstly, these are tall column heaters that make it difficult to get feet above the stones. As with Iki, Narvi, Helo, Harvia and others I recommend avoiding all tall column heaters in most cases. Homecraft column heaters also have the heating elements enclosed in a round steel cage. The stated purpose is to protect them from damage caused by shifting stones or chlorinated water. I don’t believe either of these has been a significant problem, at least in Finland/Europe, where electric heaters with stones directly against the elements routinely last for decades. When it is a problem, such as Huum, it appears to be from poor engineering and using lower quality elements. Some concerns with this design include;
- Heat source to stone interface – Stones packed directly against the elements results in good heat xfer to the stones. The cage likely results in less. Saunum for instance uses multiple cages that result in greater heat source to stone interface. Narvi have recently introduced their Heat series that includes protected elements but a primary purpose here is to be able to replace them without re-stacking all of the stones.
- Radiant – The Apex produces about 2x more radiant than comparable heaters from Iki, Narvi and Helo. Heat is a zero sum game, any heat becoming radiant (that we don’t want) is heat that is not heating the stones to produce convective heat and steam (both of which we do want). The Revive produces less radiant so may perform better.
- Steel steam rather than stone steam – Unprotected elements have little surface area and nearly all of this is vertical so only perhaps 1% of steam is made from the elements and 99% from stone. With the Homecraft design (below) there is a large flat steel plate about 8-10cm below the top of the heater. Even if these stones are well over 200°c most of the water will fall through to the steel plate with most of it then likely becoming steel steam. The remainder likely flowing off to the sides and hopefully becoming stone steam.
- The proof is in the pudding – In the end the important thing is how it performs. Does it produce a good convective loop? Little radiant? Good gentle but intense stone steam? Even with the concerns above these may be acceptable sauna heaters. Hopefully some tests in the near future to see.
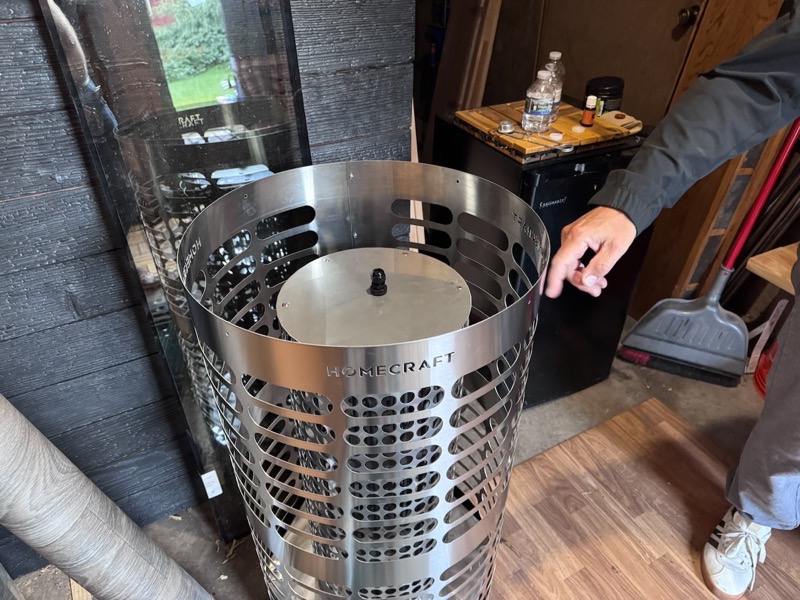 Homecraft heater with steel plate
Homecraft heater with steel plate
- Kuuma – These appear to be excellent build quality from a company with a reputation for quality products but are not really sauna heaters. These produce more radiant heat than is desired in a sauna, not as much convective heat nor convective air flow, and produce steel steam that can sting or bite rather than the intense but gentle steam that sauna is known for. With the very limited stone depth, no airflow up through the stones and non steam producing stone temps of only about 105°c when they s/b about 150-250°c, the stones in a Kuuma are purely decorative rather than functional. The lack of a good convective loop results in increased stratification. The new Kuuma Blue Flame is an improvement but still falls far short of a real sauna heater and is too tall. If they introduce the Kuuma Air I’ll likely be a hearty supporter as I’d like to see a good sauna heater manufactured by a U.S. company.
- Royale, Grill’D, Other – I don’t know about the build quality of these. Similar to Kuuma these do not appear designed to function well as sauna heaters. Grill’D for instance is 500mm (20”) to combustibles on all sides which is a lot of radiant heat. 3-6” is good with as much as 10” perhaps acceptable for home saunas.
- Ilo – These appear to have a few problems. Topping the list is lack of stone mass/depth above the heat source. We need about 14” or more depth (by perhaps 14” diameter) of fully heated (150°c or higher) stones to create good steam, Ilo has only about 4” depth so much of the water is likely to flow through the stones and down on to the elements. Ilo also likely lacks enough active stone height to create a good convective loop. If the Ilo allowed for stones among the elements it would function better and perhaps similar to a Narvi NS Mini.
- Scandia – Makes gas and electric heaters. These heaters lack sufficient stone depth and so produce harsher steel steam rather than gentle stone steam. They lack air flow up through the stones (and even tout their ’solid tray’ as a feature) which results in a weak convective loop. They lack sufficient stone mass overall which results in faster cycling and temp changes rather than more gradual and comfortable heat. As currently designed these are not a good choice.
- Am-Finn – Same as Scandia
- Huum – Nobody should support this company for any of their products. They have shown themselves to be lacking in integrity, ethics as well as any sense of quality design, testing and manufacturing. I was a fan of Huum and recommended them here and for some specific projects. Two things changed my mind. The first was that they are not properly UL listed which puts anyone in the U.S. using their electric heaters at significant financial risk, they have been dishonest about this and have so far refused to get properly listed. The second was how they treated their U.S. customers with regard to elements burning out very prematurely.
- Heating elements that last less than a year when other mfr’s last 20 to 50.
- Not covering the elements under warranty including refusing such requests from their dealers.
- March 2023 Update: After over 3 years of considerable bad press, including here, they did finally acknowledge the problem and have provided replacement elements for some customers. They have not pulled the bad products from market though.
- May 2023 Update: They have provided some customers with a kit that they claim will alleviate the problems. Given their history we’ll have to see if this solution works both in element longevity and without reducing heat/steam function.
- May 2024 update: There have been several reports and photos of the kits that protect the elements warping quite badly.
- Heating element failure potentially increases fire risk. There has been at least one report of a Huum heater catching on fire, including video of the fire. Several people have posted photos of significant burning of wood walls near Huum heaters.
- There have been increasing reports of the stones they supply (and I believe require to have any warranty) breaking down very quickly (and they are round which creates other problems). Similar to the failed elements they have recently begun to replace these. How such bad stones got included in shipments is a question but at least with this one they stepped up.
- Putting their customers at significant risk of financial ruin by skirting UL regulations and being intentionally deceptive about it. They appear to have gotten approval for use as a general heater but not as a sauna heater under UL875 guidelines. This is not only unethical but could result in consumers not being covered by insurance in case of a fire as using one of these in a sauna likely goes against UL and National Electrical Code regulations. Someone’s house could burn and insurance might not cover any of it. This is, in my opinion, the biggest concern with this company – both the risk they are putting on their customers and the lack of integrity that it shows. Worse, when directly pointed out to them online they have defended what they are doing. I disagree with the UL standards but putting customers at risk like this is not the way to deal with it.
- In March 2023 their founder posted on forums that the problems of premature element failure was due to customer mis-use, not a design or quality failure on the part of Huum. Interestingly no other manufacturer, including Harvia and other value brands, has had such problems of customer mis-use.
- Jun 2024 – The original concerns about Huum quality problems were included here in 2020 with further bits added over the post-ceding months and years. As of June 2024 problems are still appearing with some regularity. Customer service from Huum seems spotted with some having good results on getting warranty replacement and others not. Given their track record it’s doubtful Huum will provide much service after the warranty period.
- All that said, Lassi did find the Huum Drop to provide a good sauna experience with good steam: HUUM DROP 9kW Heater: The fast lane to soft steam.

If these made for good sauna heaters they’d be popular in Finland, Germany and elsewhere. But they’re not.
The only place they are salable is North America – two countries with the lowest sauna use of all developed countries.
Why is that? Why would people in Finland not buy one of these?
- They produce too much radiant heat.
- They produce too little convective heat resulting in a weak convective loop.
- The Steam can be too hot, harsh or stinging feeling.
Radiant – A lot of the heat produced by the fire goes in to the steel instead of the stones and the steel then radiates that heat to bathers. That’s fine when we’re trying to heat people in a normal room where radiant is desirable or in a Russian Banya where radiant is expected and part of the experience, but is the opposite of what we want in a sauna.
In a sauna we want the heated mass to be the stones, not the heater itself. With good airflow up through the stones, the stones are fairly efficient in creating the convective heat that we want in a sauna, plate steel is not. This is why the best sauna heaters are intentionally made of such thin material. A Narvi NC isn’t light because it’s cheap or as some Americans disparagingly call it ‘a tin can heater’, it’s light because that makes for the best sauna heater with very little radiant that results in the best sauna experience.
Poor Convective Airflow – Another problem, and one perhaps more important than the radiant heat, is lack of convection airflow up through the stones to drive a convective loop. This airflow is critical for bather comfort, removing CO2, cooling our skin, reducing stratification and other bits. It is the core of a sauna experience and why the International Sauna Association calls sauna a ‘hot air bath’. This isn’t a universal problem with all heavy steel stoves. Nippa for instance has added vents in the bottom of their stone basket to allow for this critical airflow.
Stinging Steam – The steam can be too hot and feel harsh rather than gentle. Some describe it as ‘stinging’ or ‘biting’. In a Kuuma for instance, due to the limited stone depth and stones not getting hot enough, when you throw water on the stones a lot of it can flow down to the steel of the firebox resulting in steam that is produced faster and is hotter feeling. Larger stones likely make this worse, smaller likely better. In a sauna heater, water should ideally touch only stones to become steam and never touch steel.
Evenness of Heat – Stones retain heat better than steel and so do a good job of evening out the temperatures in a sauna. Steel gains/looses heat faster and can exacerbate temperature swings. This is another benefit to sauna heaters that have their thermal mass focused on the stones with very little thermal mass of steel.
Before continuing, let me say this. There are people in North America who have Kuuma’s or similar stoves and love them. I’ve done rounds with some of them and had an enjoyable time. It’s just not a sauna experience. It’s not the same compelling experience that has made sauna so popular throughout much of Europe. If you want a sauna experience, the same experience that people in Finland enjoy, then you need a sauna heater, not a heavy steel stove.
A well designed heavy steel stove with air channels in the sides and perhaps some convection fins that reduce radiated heat and carry that heat up through the stones can likely work OK in larger saunas of perhaps 300x300x300cm (12’x12’x12’) but not so well in smaller saunas where the heater is closer to bathers. So while it’s tempting to weld a stone basket to an old steel wood stove to use in a sauna, there’s a bit more to it.
More: Why Wood Stove Conversions Fail.
And for a bit of fun. I presume this was created by the folks at Kuuma: https://trumpkinsauna.com. I must admit, it’s pretty funny.
Converting a Heavy Metal Stove to a Sauna Heater – Perhaps A good way to understand the differences in a heavy steel stove and a sauna heater might be to look at how we’d change the design. Let’s start with a Kuuma.
 A Narvi NC (left) vs Kuuma (right) – Note the firebox location and how much more space is dedicated to stones in the Narvi, particularly height that is about 3x what Kuuma has. Narvi also routes the flue in a way to get the stones as hot as possible. This all makes a critical difference in the sauna experience.
A Narvi NC (left) vs Kuuma (right) – Note the firebox location and how much more space is dedicated to stones in the Narvi, particularly height that is about 3x what Kuuma has. Narvi also routes the flue in a way to get the stones as hot as possible. This all makes a critical difference in the sauna experience.
Heat production is a zero sum game. If the fire is producing 24kW then that’s all we’ve got to work with. Any of that 24kW that becomes radiant heat is heat that is not available to heat the stones. In a sauna heater we want as much heat as possible to go in to the stones.
Of 24 kW of heat the fire produces, the standard Kuuma produces in to the sauna perhaps 2 kW convection / 18 kW radiant / 3 kW conductive*. Ideally we want 24/0/0 but that’s impossible so maybe 19/3/1 (with 1kW still going up the flue) would be a good realistic target (the first two below are I think the easiest changes to get the most bang for our buck).
- It has some stones but little airflow so we’ll add airflow vents, about 2” high, along the entire bottom of all of the sides of the stone basket. Now we’re at perhaps 4 kW / 16 kW / 3kW
- It has quite minimal stone depth and mass (both are critical) so let’s add about 12” of height to the stone basket. So now we’re at maybe 8/12/3. This also reduces some problems of too hot or stinging steam from water hitting the steel below the stones.
- Let’s route the flue through the stones in a way to extract a bit more of that heat to become convective. Now we’re at 10/12/1.
- If we add the std Kuuma heat shields we get to maybe 12/10/2. We know the Kuuma is still producing a lot of radiant because its clearance to combustibles with a heat shield is 15-18” on the sides and 48″ in the unshielded front, a good bit more than the 4-11” of Narvi, Helo, and Harvia’s various wood heaters. Our stove is now beginning to generate enough convective heat to start forming a little bit of the löyly cavity that is critical to a sauna and should aid in reducing CO2.
- Heat shields are actually not what we want though. We want to convert heat energy to convective heat, not just try to shield it. So we need to think differently. Let’s make the heat shield thinner, remove the insulation on the inner side and make sure we have good air flow. This will allow the air moving up in the channel between the firebox and heat shield to take on more of the heat and carry it up as convective heat. Yes, it will also now be taking on more radiant from the firebox but this s/b less than is being converted to convection so we’re good. Now we’ve got perhaps 13/9/1.
- Instead of the std heat shields let’s do a permanent shield fully surrounding it and make it with a lighter material that won’t transmit as much heat from the firebox out to the surface of the outer carcass. This can be done in a way that preserves the big iron Kuuma aesthetic. So now we’re perhaps 17/5/2 and have a pretty good convective loop and löyly cavity.
- Making the stone basket out of lighter material will reduce radiant here a bit. So maybe 18/4/1
- The top of the stones are really high (44″) which will force the löyly cavity it’s now producing up quite high and thus require the benches to be much higher than normal (≈52” foot bench and 68” sitting bench) so let’s take a bunch of steel off the bottom to lower everything down and get a side benefit of a bit less steel mass to give us our 19/3/1.
* This is NOT calculated scientific but should give a general idea of the differences in a heavy steel stove vs a sauna heater and why sauna heaters are made the way that they are. I have intentionally kind of ignored conductive and advective heat which are not significant in this scenario and assigned a value of 1kW.
I did not include that a Kuuma has fire brick while sauna heaters do not. This is a much more complicated topic. One bit is that convection transfers heat from the heaters much faster than radiating does so sauna heaters don’t need the fire brick while a Kuuma does. But there’s more to it and I’m not sure that any of it has an impact on performance.
Path Of Least Resistance – Heat takes the path of least resistance towards cooler temps. A well designed sauna heater makes the path of least resistance be towards the stones. And, by using thinner metal, makes becoming radiant heat higher resistance. Heavy steel is a path of lessor resistance so a heavy steel carcass becomes the path of least resistance with a Kuuma. So much of our valuable heat is becoming radiant rather than going in to the stones to produce convective heat and steam.
Steel vs Stones – One issue that’s been raised about Kuuma and similar stoves is that the steam is more harsh, stinging or biting compared to the intense but gentler steam from Narvi, Iki, Helo, Harvia and other sauna heaters. This is likely primarily due to the limited stone depth above the firebox that results in much of the steam made by steel rather than stones. Water hitting steel results in steam being produced faster with the result being much greater density of steam molecules at our head and upper torso that feels much hotter. We’ve also experienced a much faster change, rather than 0-60 in 5 seconds we’ve gone 0-200 in 2 seconds.
Steel can also result in the steam being superheated. So rather than 100°c, it might be 150-200°c. With a sauna heater we’ll typically see a quick drop of ≈10-15°c in temperature above the heater when we pour water on to make steam. This is largely because a bunch of 100°c steam is mixing with 150°c hot air resulting in a 140°c mix. In one case with a Kuuma pouring water on resulted in a 30°c increase which I believe could only be caused by the steam having become superheated by the steel plate. (note that this heat is different from the latent heat of vaporization embedded in the steam).
Some thermal images of Kuuma’s have revealed another possible problem in that the stones don’t get very hot. Below, after 5 hours of heating, they are only ≈104°c when they should be at least 150-250°c or more. The result is that here almost no steam is produced by the stones as it should be so nearly all of the water drops down to the steel firebox where the steam is produced by steel instead. I don’t know if the problem of stones not being properly heated is a problem for all Kuuma’s or only some.

As well, some studies have shown that water on stones produces steam with beneficial negative ions while water on steel or iron produces undesirable positive ions*. If accurate then the lack of stone depth, airflow up through the stones and greater likelihood of water hitting the steel carcass will be a concern with Kuuma and similar stoves. How much of an issue this is in reality I don’t know but it’s worth further investigation.
Unpleasant? Not necessarily, but it’s more of a Banya experience than a Sauna experience. With a Kuuma you are not getting what people in Finland and elsewhere value in a sauna heater.
Perhaps they can call the original Kuuma the Kuuma SC (Sweat Cabin) and this new one from above can be the Kuuma Air 🙂

Since I published the above, Kuuma have introduced two new products to address some of the issues raised above. In addition to the Original (above left) they now offer the Blue Flame (center) and LP or Low Profile.
The Kuuma Blue Flame will likely help a bit on #1 and perhaps very minimally on #5. So better but it still does not appear that it will perform like a sauna heater. It still has a very high fire box and a lot of exposed steel that could produce a lot of radiant heat. The latest design I’ve seen appears to include an integrated heat shield (#6) made of much thinner material that also wraps around the corners so that should help as well as the lighter stone basket (#7). The proof will be in the pudding when we see how the final design performs in a sauna. One key is to remember that the foot bench (and bathers feet/legs) should be 4-8x the distance to combustibles from the heater. So if the distance to combustibles is 200mm (8”) on the side then the foot bench should be no closer than 800mm (32”) and ideally about 1600mm (64”) from that side.
Kuuma Low Profile (LP): The new Kuuma LP is a big step forward but still falls short of being a good sauna heater.
It produces less radiant than the original Kuuma but with 10” of clearance required to combustibles it still produces about 2x as much as the Iki Original (4”) or Narvi NC, Velvet or Stoney (all 5.9”). It is however about equal to or better than some of the value heaters from Harvia and others (that people in Finland tend to avoid if they can afford to because of the radiant heat).
It has too little stone depth and mass above the fire box (active stones). This should be at least 14” of depth but ideally a bit more. As we discussed above, the lower stones in an open mesh heater are decorative and provide no real functional purpose. Stones higher up on the side of the fire box help to reduce radiant which is important but are worth only about 1/10 what a stone above the fire box is for producing convective heat and steam. The critical stones for producing convective heat, steam and thus löyly are those that are in excess of 150°c which are those above the fire box and this still appears too minimal with the LP. The steam should be better than the original but still likely more harsh than what is expected of a good sauna heater in Europe.
We also don’t know how well the active stones are being heated. A simple flat top plate on the fire box is likely not sufficient. Designing the top of the firebox to efficiently xfer heat energy to the stones is critical. Narvi and Iki for example utilize circuitous flue arrangements to do this. Inverted steel fins or cones might work well also.
The lack of active stone depth and mass can result in a poor convective loop, less even temperatures, harsher steam, and positive ions. Ideally water should touch only stones and never any steel. Kuuma could perhaps offer an extension that would result in ≈13-16” stone depth above the fire box to help with this but would need to insure that all of the stones are properly heated. Without lowering the firebox this would be a very tall heater.
One final point. The foot bench in a sauna needs to be at least 85cm (≈34”) high, regardless of heater height, in order to be above the cold zone. An overall heater height of 30” then isn’t a problem and shorter not really a benefit.
Is There A Way To Have A Heavy Steel Kuuma, Nippa or other Stove Work? – Possibly. With some effort. If we look at our list of attributes of a sauna in the beginning of Trumpkin’s Notes on Building a Sauna we’ll see that we need good convective airflow, even temps, no noticeable radiant, gentle steam, fresh air, etc. I was recently in a space heated by a Kuuma that had somewhat successfully blocked radiant from most seating positions. It still lacked convective airflow though (I was hoping that the stove alcove would produce enough but that didn’t happen) which resulted in kind of burning skin and poor ventilation. As with other Kuuma’s the steam was more harsh than the gentle steam of sauna heaters. Even with a fresh air supply vent on the far side under the benches pulling a good bit of air the CO2 levels were in excess of 3000 ppm and quite uncomfortable.
In theory;
- Have a short wall between the stove and bathers to block direct radiant heat.
- Do NOT add a ‘wall of heat’ of stone or other material on the wall behind the heater. Do whatever is necessary for fire safety but no more. You do not want to reflect radiant on to bathers.
- We need convective airflow up through the stones and a convective loop so we need to modify the stove by adding some vents to allow significant airflow in to the bottom of the stone basket.
- We likely need to increase the height of the stone basket for more stones, more convective airflow and so that steam is produced from stones and little or no water reaches the steel below.
- Ventilation to keep CO2 levels below 700 ppm.
This MIGHT work to have a sauna experience using a heavy steel stove. I don’t know if cutting vents in the stone basket or increasing the height would cause any problems. This might not result in a sufficient enough convective loop and the loop may not go low enough to reach bathers feet. It might be necessary to reduce the overall height of the stove to get the top of the stones lower.

Consideration For Others – If you’re debating between wood and electric heat, give some consideration to your neighbors. While wood is enjoyable and romantic, it does not otherwise make for a better sauna. An electric sauna has every bit as good of heat, löyly and overall environment along with some great convenience benefits. Many Finns actually prefer electric as the heat is more even. If you live close to others please give some consideration to how smoke, even if legal for you to do, might negatively effect them. This is in response to someone’s concern that neighbors might complain:
Just because you have a right to do something doesn’t mean that you should. Personally I think that attitudes like this are at the core of many of the conflicts we’re seeing in the communities around us and this certainly doesn’t help the reputation of sauna.
—
* When stones are heated, thanks to the piezoelectric effect, the breakdown of weaker mineral bonds, any steam created is likely to produce negative ions. Materials like stone will tend to donate electrons (electrons have a negative charge) to the water or steam resulting in molecules with an extra electron such as O₂⁻ or OH⁻.
On the other hand, when steel oxidizes it will tend to produce positive ions in to the steam. Rather than donating electrons it holds on to them (oxidation). It also then produces Fe²⁺ or Fe³⁺ ions in to the steam.

